Blood Pressure




Discover a wide range of effective blood pressure medications and monitoring devices designed to help you maintain healthy levels and support your cardiovascular health. Shop trusted brands and find the best solutions tailored to your needs.
Blood pressure management is crucial for cardiovascular health. High blood pressure, or hypertension, affects millions worldwide. Proper medication can control blood pressure and reduce risks of heart attack, stroke, and kidney damage. Many medications are available, each with different mechanisms and uses. Below is a review of popular blood pressure drugs commonly found in online pharmacies.
Aceon (Perindopril) is an ACE inhibitor. It helps relax blood vessels and lowers blood pressure by blocking the formation of angiotensin II. Aceon is effective and usually well-tolerated. It may cause cough and increased potassium levels in some patients. Regular monitoring is needed for kidney function.
Adalat (Nifedipine) is a calcium channel blocker. This medication relaxes the muscles of your heart and blood vessels, lowering blood pressure. It works fast and is useful for patients with angina as well. Extended-release versions help maintain steady blood pressure throughout the day. Common side effects include swelling and flushing.
Aldactone (Spironolactone) is a potassium-sparing diuretic. It reduces fluid buildup by helping the kidneys remove excess salt and water without losing potassium. Aldactone is often used for resistant hypertension and heart failure. Watch for signs of high potassium and breast tenderness in some patients.
Altace (Ramipril) is another ACE inhibitor. It effectively lowers blood pressure and offers heart protection. Patients taking Altace may experience dizziness or dry cough. Blood tests to monitor kidney function and potassium are important during treatment.
Avapro (Irbesartan) belongs to the angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARBs). It blocks harmful hormone effects that narrow blood vessels. Avapro is an alternative for patients who cannot tolerate ACE inhibitors. It helps reduce blood pressure steadily and is generally well tolerated.
Beloc (Metoprolol) is a beta-blocker. It lowers heart rate and the heart's workload. Beloc is useful for patients with hypertension and certain heart conditions like angina or arrhythmias. Side effects can include fatigue and slow heartbeat. Extended-release options offer convenience.
Benicar (Olmesartan) is an ARB. It provides effective blood pressure control without many of the side effects seen in other drugs. Benicar can protect kidneys in diabetic patients. Headache and dizziness are common mild side effects.
Calan and Calan SR (Verapamil) fall into calcium channel blockers. They are used to treat hypertension and certain types of angina. Calan SR is the slow-release form for once or twice daily dosing. Watch for constipation and swelling of ankles.
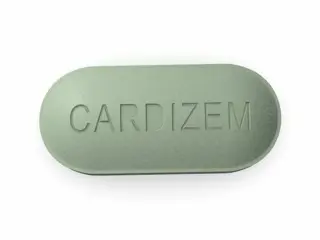
Cardizem (Diltiazem) is also a calcium channel blocker that works by relaxing blood vessels and reducing heart rate. It is used for hypertension and angina. Side effects may include headache and dizziness. Extended-release forms allow steady blood pressure control.
Cartia XT is a long-acting diltiazem preparation. It offers similar benefits but ensures stable medication levels over 24 hours. Patients should avoid abrupt stopping to prevent rebound hypertension.
Catapres and Clonidine are central alpha agonists. They reduce nerve signals that tighten blood vessels. These drugs are effective but may cause dry mouth and sedation. Clonidine can be used in resistant hypertension but should be discontinued carefully to avoid spikes in blood pressure.
Combipres is a combination pill that includes clonidine and a diuretic. This combo balances fluid removal with nerve relaxation. It is convenient for patients needing multiple approaches to hypertension treatment.
Coreg (Carvedilol) is a non-selective beta-blocker with alpha-blocking activity. It is commonly prescribed for hypertension and heart failure. Coreg reduces heart rate and dilates blood vessels. Side effects include fatigue, dizziness, and slow pulse.
Coversyl (Perindopril) works like Aceon in the ACE inhibitor class. It reduces blood pressure and offers protection against heart and kidney damage. Regular follow-up is necessary to monitor side effects.
Cozaar (Losartan) is an ARB widely used in hypertension management. It prevents blood vessel narrowing, reducing strain on the heart. Cozaar also lowers the risk of stroke in some patients. Side effects are generally mild.
Diltiazem and its forms are versatile in hypertension treatment. They reduce heart workload and relax arteries. Patients should inform doctors if they have heart rhythm problems, as diltiazem can worsen these conditions.
Esidrix (Hydrochlorothiazide) is a thiazide diuretic. It helps the body get rid of excess salt and water to reduce blood pressure. Esidrix is often combined with ACE inhibitors or ARBs. Watch for dehydration and low potassium.
Frumil combines a loop diuretic (furosemide) with hydrochlorothiazide. This potent combination is reserved for patients with resistant hypertension or heart failure. Close monitoring of electrolytes is essential.
Hytrin (Terazosin) is an alpha-blocker. It relaxes blood vessels and helps the bladder in cases of enlarged prostate. It lowers blood pressure but can cause dizziness, especially after the first dose.
Hyzaar combines losartan and hydrochlorothiazide. This pill targets different pathways to improve blood pressure control. Combination therapy often results in better compliance and results than single agents.
Inderal and Inderal LA (Propranolol) are beta-blockers. They reduce heart rate and blood pressure. These are useful in hypertension, angina, and certain arrhythmias. Side effects include fatigue and cold extremities.
Isoptin and Isoptin SR (Verapamil) are calcium channel blockers. They are effective for blood pressure and rate control. Extended-release versions help with dosing convenience and maintaining steady drug levels.
Lasix (Furosemide) is a powerful loop diuretic. It removes excess fluid quickly, lowering blood pressure. Lasix is often used in heart failure and edema. Frequent lab checks are critical to monitor electrolytes.
Lisinopril is a popular ACE inhibitor. It helps relax blood vessels effectively. Lisinopril lowers blood pressure and protects kidneys, especially in diabetics. Watch for cough and possible increased potassium.
Lopressor (Metoprolol) is a selective beta-blocker with good control over heart rate and blood pressure. Useful for patients with coronary artery disease and hypertension. Side effects may include dizziness and fatigue.
Lozol (Indapamide) is a thiazide-like diuretic. It helps lower blood pressure by promoting salt and water loss. Lozol is often combined with other agents for improved effect.
Micardis (Telmisartan) is an ARB with added benefits on metabolism. It provides effective blood pressure control and may improve insulin sensitivity. Micardis is well tolerated, with low incidence of side effects.
Microzide (Hydrochlorothiazide) is widely used as a diuretic to reduce blood pressure. It works well alone or in combination with other antihypertensives. Patients should maintain hydration and report muscle cramps.
Minipress (Prazosin) is an alpha-blocker that relaxes blood vessels. It helps reduce blood pressure and may also assist in treating symptoms of an enlarged prostate. First-dose dizziness is common.
Norvasc (Amlodipine) is a calcium channel blocker. It is highly effective and usually well tolerated. It relaxes blood vessels and allows the heart to pump more easily. Swelling of ankles and flushing can occur.
Prinivil (Lisinopril) is similar to other ACE inhibitors. It helps relax arteries and prevents heart strain. Regular blood tests to check kidney function and potassium are needed during therapy.
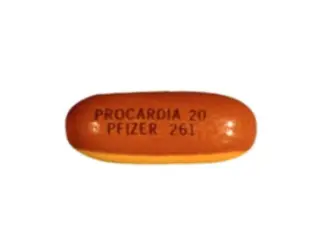
Procardia (Nifedipine) is another calcium channel blocker. Useful in hypertension and angina. Extended-release forms provide all-day control. Watch for swelling and headaches.
Tenormin (Atenolol) is a beta-blocker used for hypertension and prevention of heart attacks. It lowers heart rate and blood pressure. Side effects may include cold hands and fatigue.
Toprol and Toprol XL (Metoprolol) reduce heart rate and lower blood pressure. The extended-release version ensures 24-hour control with one daily dose. Proper dosing avoids side effects.
Trandate (Labetalol) has both alpha and beta-blocking effects. It is used in hypertensive emergencies. Labetalol can cause dizziness and fatigue but works quickly.
Tritace (Ramipril) is an ACE inhibitor with a similar profile to Altace. It helps protect the heart and kidneys while lowering blood pressure. Patients should avoid sudden discontinuation.
Vasotec (Enalapril) is an ACE inhibitor used for hypertension and heart failure. It improves blood flow and lowers blood pressure. Side effects include cough and dizziness.
Verampil and Verapamil are calcium channel blockers. They help lower blood pressure and control heart rate in arrhythmias. Extended-release forms make dosing easier.
Zebeta (Bisoprolol) is a beta-blocker that selectively slows the heart. It is prescribed for hypertension and heart failure. Zebeta is generally well tolerated.
Zestoretic combines lisinopril and hydrochlorothiazide. This combination targets blood pressure through two mechanisms. It suits patients needing dual therapy for better control.
Zestril (Lisinopril) is a conventional ACE inhibitor. It offers reliable blood pressure control and cardiovascular protection. Regular monitoring is important.
Each medication has its strengths and potential side effects. Choosing the right one depends on patient history and specific health conditions. Many patients benefit from combination therapy to target blood pressure more effectively. Monitoring blood pressure regularly and adhering to prescribed treatments are essential for managing hypertension. Talk to a healthcare provider before starting or switching medications.